- Number Of Electrons In Calcium-40
- Calcium Protons And Electrons
- Calcium Number Of Protons
- Total Number Of Electrons In Calcium
Calcium has 2 valence electrons. Calcium has 20 electrons so they are arranged 2. 2 Using orbital notation the electron structure is: 1s^(2)2s^(2)2p^(6)3s^(2)3p^(6)4s^(2) You can see that there are 2 electrons in the outer energy level and these are the valence electrons.
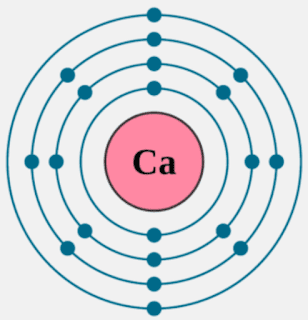
Click to see full answer
Number Of Electrons In Calcium-40
Then, why is a calcium ion smaller than a calcium atom?Because the calcium ion donates two electrons to achieve the stable state. Thus, the radius of a calcium ion is smaller than a calcium atom.
Secondly, how does a calcium atom become an ion? When it loses electron(s) it becomes positively charged and is called a cation. Calcium atom with electron arrangement K (2),L(8),M(8),N(2) loses two electrons from its outermost shell ( N shell) and forms positive ions called Calcium , Ca2+ ion.
Calcium Protons And Electrons
Each electron in an atom has a set of four quantum numbers which uniquely describe the “location” of that electron in terms of energy. For a calcium 2+ ion, there will be 18 sets of quantum numbers, not the usual 20 for a neutral atom. It will be missing the two electrons in the 4s sublevel. A calcium atom has 20 protons, 20 electrons and 20 neutrons. Calcium's atomic mass is 40.08 g/mole, which rounds to 40 g/mole. Calcium's atomic.
Calcium Number Of Protons
Then, what does calcium ion do?
Calcium in biology. Calcium ions (Ca2+) contribute to the physiology and biochemistry of organisms cell. They play an important role in signal transduction pathways, where they act as a second messenger, in neurotransmitter release from neurons, in contraction of all muscle cell types, and in fertilization.
What does a calcium atom look like?
Calcium atoms have 20 electrons and 20 protons. There are 2 valence electrons in the outer shell. Calcium is an important element for life on Earth and is the fifth most abundant element in the Earth's crust. Under standard conditions calcium is a shiny, silvery metal.

Total Number Of Electrons In Calcium
June 2018 Chemistry Regents #1-5
Highlight to reveal answers and explanations
Questions | Answer | Links | Explanations |
| 1 Which statement describes the charge and location of an electron in an atom? (1) An electron has a positive charge and is located outside the nucleus. (2) An electron has a positive charge and is located in the nucleus. (3) An electron has a negative charge and is located outside the nucleus. (4) An electron has a negative charge and is located in the nucleus. | 3 | electrons...negative...outside nucleus protons....positive...in nucleus | |
| 2 Which statement explains why a xenon atom is electrically neutral? (1) The atom has fewer neutrons than electrons. (2) The atom has more protons than electrons. (3) The atom has the same number of neutrons and electrons. (4) The atom has the same number of protons and electrons. | 4 | neutral...postive equals negative protons equal electrons | |
| 3 If two atoms are isotopes of the same element, the atoms must have (1) the same number of protons and the same number of neutrons (2) the same number of protons and a different number of neutrons (3) a different number of protons and the same number of neutrons (4) a different number of protons and a different number of neutrons | 2 | isotopes...same number protons different number of neutrons | |
| 4 Which electrons in a calcium atom in the ground state have the greatest effect on the chemical properties of calcium? (1) the two electrons in the first shell (2) the two electrons in the fourth shell (3) the eight electrons in the second shell (4) the eight electrons in the third shell | 2 | valence electrons are the ones that determine chemical properties highest energy level electrons | |
| 5 The weighted average of the atomic masses of the naturally occurring isotopes of an element is the (1) atomic mass of the element (2) atomic number of the element (3) mass number of each isotope (4) formula mass of each isotope | 1 | definition of atomic mass |
